AchilleS Vaccines Projects
We are committed to designing new products that tackle some of the largest current world health issues
Solutions to fight AMR pathogens
Neisseria meningitidis is a Gram-negative encapsulated bacterium that causes bacterial meningococcal meningitidis epidemics worldwide. Meningococcal disease has high epidemic potential with clusters and outbreaks occurring worldwide. Explosive epidemics can occur in the “meningitis belt”, an area of sub-Saharan Africa with a population of >400 million extending from Senegal to Ethiopia, with incidence rates over 1000 cases/100 000 population. The disease can be rapidly fatal and can leave severe disability, making treatment difficult. Survivors often suffer neurological impairments such as motor weakness, paralysis, incoordination and cognitive deficits. Loss of limbs due to haemorrhagic necrosis is also common. Due to the fast escalation of symptoms, prompt treatment is often difficult and vaccination remains a priority in order to tackle mortality, morbidity and sequelae. Current vaccines are expensive to produce, in some cases reactogenic, and/or offer limited range of coverage against meningococcus strains. AchilleS Vaccines will design and produce a pan-meningococcal vaccine that will harness the remarkable features of modified mOMV and will be devised to contain strain-specific and cross-reactive antigens against a multitude of strains of Neisseria meningitidis of clinical relevance. Therefore, the vaccine will uniquely provide multivalent broad coverage against all the major serogroups responsible for meningococcal meningitis worldwide. The flexibility of the mOMV plarform will also allow “plug and play” modifications and/or inclusion of new antigens to increase valency and coverage in response to epidemiological changes. The project will deliver a new safe, effective, versatile, multivalent universal pan-meningococcal vaccine based on the mOMV platform. The vaccine will have low production costs and will be easy to scale-up for production and rapid commercialisation. Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) is a Gram-negative human pathogen that causes approximately 80 million infections of mucosal surfaces including urethra, endocervix, pharynx, conjunctiva and rectum. The disease spectrum ranges from mucosal inflammatory disease to pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID) that, after resolution, can leave sequelae such as male and female sterility, chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, low birth weight, septic abortion and acute conjunctivitis/blindness in the new-born. Bloodstream infections lead to septic arthritis, endocarditis, meningitis and in some cases death. Gonococcal infections are prevalent worldwide with a disproportionate burden in Low-Middle-Income countries (LMIC). Neisseria gonorrhoeae acquires resistance to antibiotics very rapidly and there is no longer a single reliable class of antibiotics for empirical treatment of these infections. The Center for Disease Control (CDC) ha categorised gonococcus as one of the “urgent” antibiotic-resistant threats in the USA. There are currently no effective vaccines against gonococcal infections. This is due to the complexity and antigenic diversity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that is able to evade and suppress immune responses. Therefore, efforts need to move towards a vaccine that can overcome these immune-suppressive constraints. The flexibility of the mOMV plarform will also allow “plug and play” modifications and/or inclusion of new antigens to increase valency and coverage in response to epidemiological changes. Salmonella are bacteria that cause life-threatening diseases in adults and children. The global estimated burden of typhoid fever is over 21M illnesses and 200,000 deaths with sustained high incidence in South East Asia and endemic/epidemic occurrence in Africa. Paratyphoid causes 5.4M illnesses worldwide. Invasive non-typhoidal serovars (iNTS) are a leading cause of lethal sepsis and severe relapsing infections in young children and immune-compromised individuals, especially in countries of the sub-Saharan African region with an estimated 3.8M illnesses, 680,000 deaths annually and very high case-fatality ratios (20%). These diseases co-exist in many geographical areas, especially in Low and Middle Income Countries (LMIC). Therefore, a single vaccine against all the major Salmonella infections would be highly desirable. The project, funded by the Wellcome Trust, will use genetically engineered mOMV to target various salmonella-related infections in a single vaccine preparation. The vaccine will have the advantages of efficacy, multivalency, safety and low production cost and will therefore benefit both travelers and those who live in endemic areas.
Categories :
At AchilleS Vaccines we will exploit the potential of mOMV to overcome many of the constraints that have so far impeded progress towards gonococcal vaccines. The type of immune responses induced by mOMV and the possibility to use bioinformatics to identify of antigens that are conserved among Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates and can elicit functional bactericidal responses, will pave the way towards development of low-cost, versatile, multivalent gonococcal vaccines.
Categories :
Categories :
Covid-19 and Malaria
Former Projects
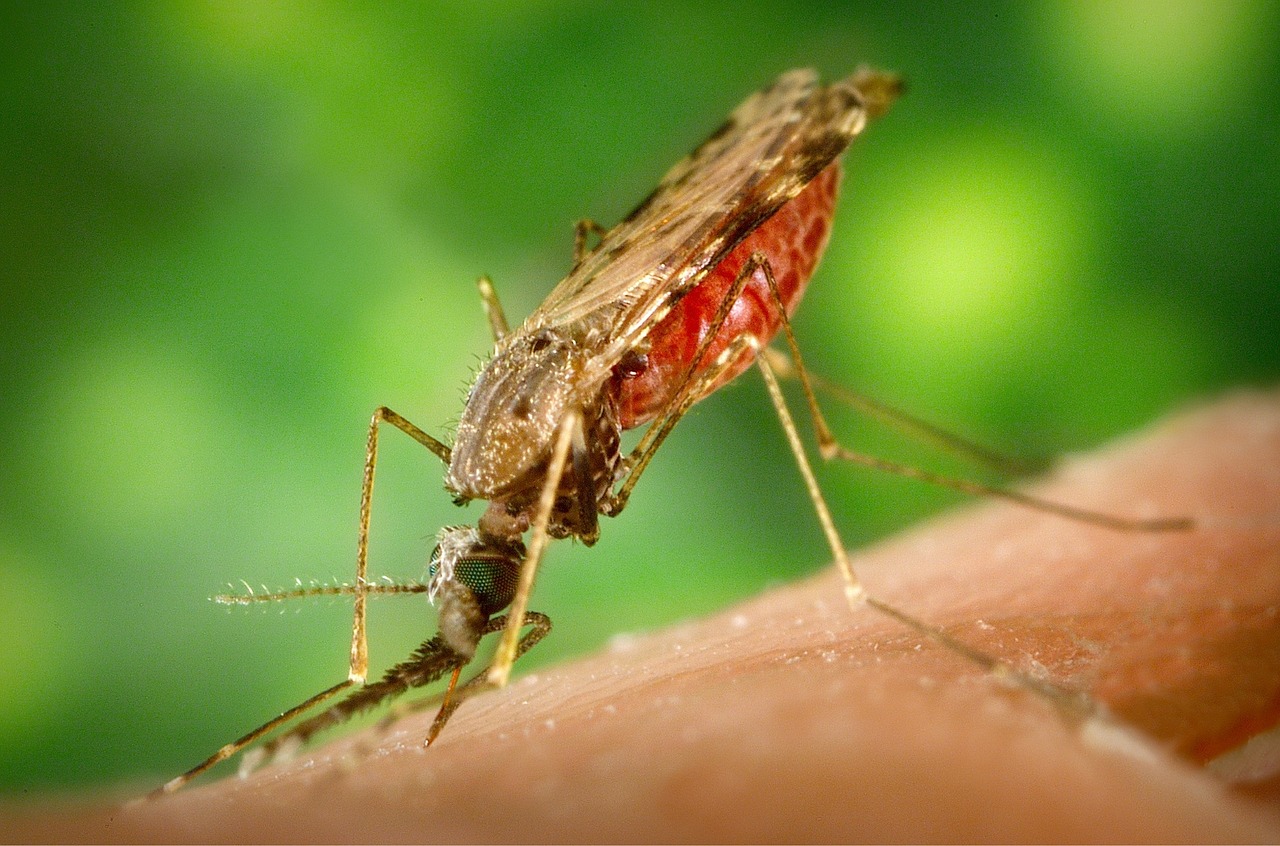
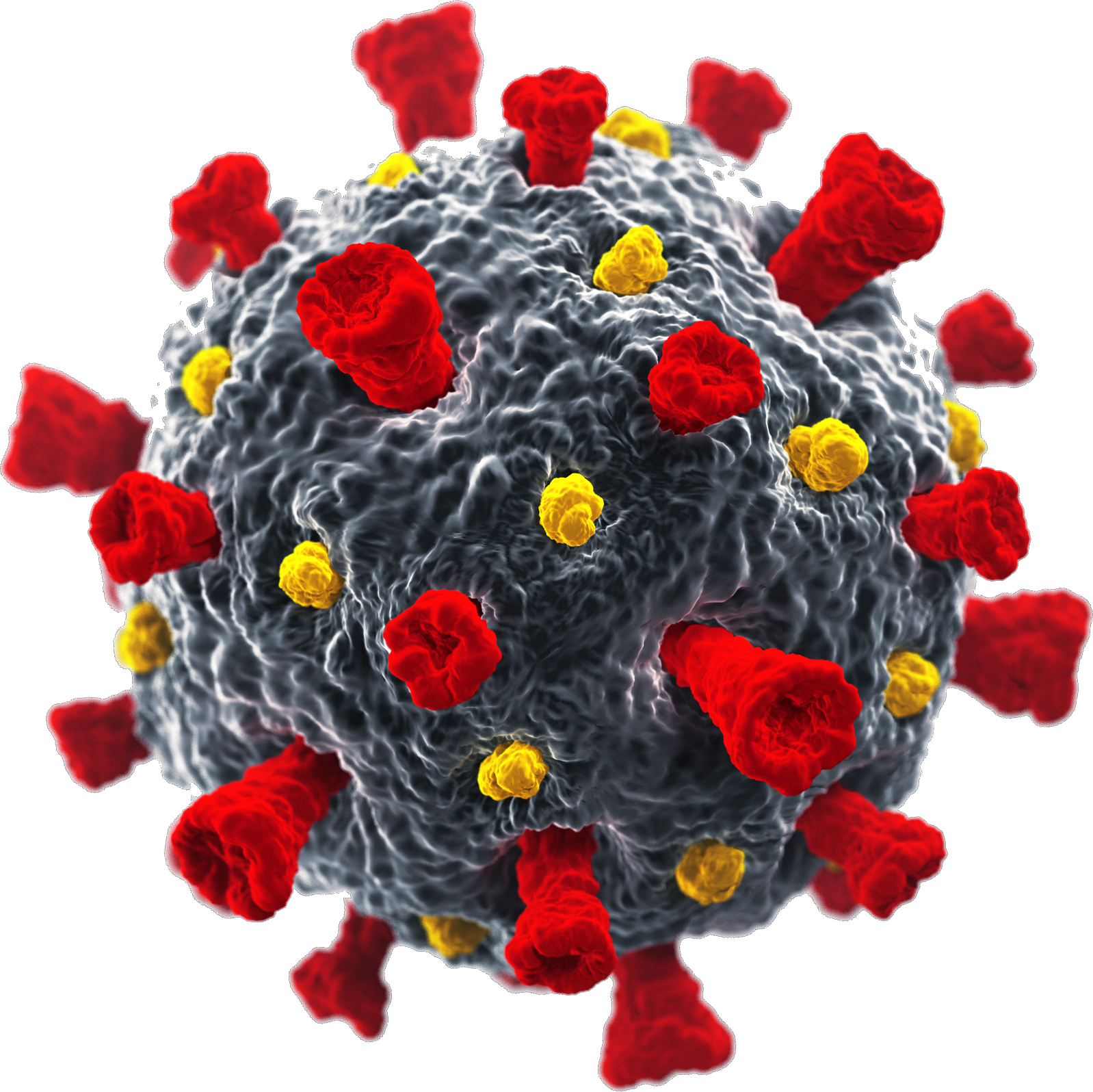
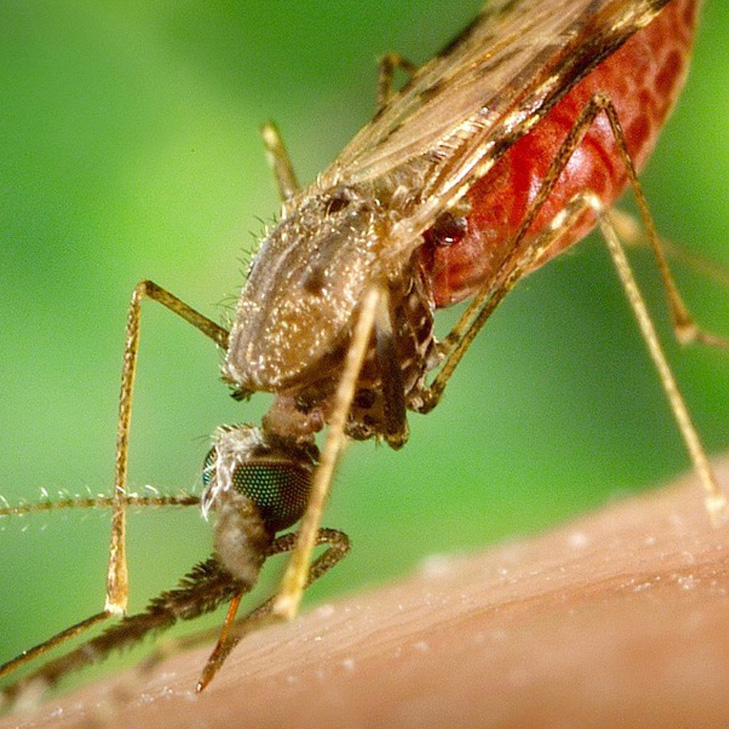
SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, is a respiratory Coronavirus that has rapidly spread worldwide to pandemic levels becoming a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. On the 11th February 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that the respiratory disease caused by 2019-nCoV had been officially named Covid-19 (Corona Virus Disease 2019). Covid-19 infection has a high death toll especially, but not exclusively, amongst elderly patients with pre-existing comorbidities. No vaccines, immune therapeutics or effective drugs are currently licensed against Covid-19. Even if a successful solution were found, it is expected that significant time will be needed for large-scale implementation of immunization programs. Vaccines are a long-term solution against emerging infections. However, in an emergency situation such as the Covid-19 pandemic, monoclonal antibodies are a pivotal tool that can be used for immediate therapy of any patient testing positive for the virus, and to provide immediate protection from infection in high-risk individuals for a number of months. Antibodies are proteins generated by the immune system. They are one of the host resistance mediators against infection. Antibodies can be used for the treatment of infectious diseases, cancer and autoimmune syndromes. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are derived from identical host immune cells that originate from a single progenitor B-lymphocyte that recognizes a single molecular structure. Monoclonal antibodies can be manufactured at commercial scale using the appropriate cell-based expression systems. These human-derived proteins are a valuable pharmaceutical remedy to cure and prevent disease. mAbs are one of the most effective pharmaceutical remedies in modern medicine. Only few of about 100 currently licensed mAbs are for use in the treatment of infectious diseases. However, in the future mAbs are expected to play a key role in curing and preventing infectious diseases especially those caused by emerging pathogens and microbes that exhibit an increasing level of antibiotic resistance. The MAbCo19 project aims to rapidly deliver a human neutralizing monoclonal antibody as prophylactic and therapeutic tool against Covid-19. Human antibodies have proven to be powerful solution for diseases like HIV, RSV and recently provided the first cure for Ebola. The project will exploit cutting edge technology, where B-cells from Covid-19 convalescent patients are selected for their ability to produce high-affinity antibodies. The genes encoding these antibodies are cloned in appropriate expression (antibody-production) systems, followed by preclinical evaluation of their protective efficacy and further rational engineering to achieve maximum therapeutic efficiency. MAbCo19 is engineered to have a high virus-neutralizing potency and it will be easily administered via the intramuscular route. This special project is funded by EU Malaria Fund and is conducted in cooperation with Dr. Rino Rappuoli’s “MadLab” based at the Toscana Life Sciences Foundation (TLS). This is the only AchilleS Vaccines, jointly with TLS, are coordinating highly experienced organizations such as Menarini Biotech S.r.l. and Istituto Biochimico Italiano Giovanni Lorenzini S.p.A to ensure the rapid pharmaceutical development and manufacturing, according to the cGMP criteria, of the first clinical batch, thus completing an Italian consortium from the R&D laboratory to clinical studies. Subject to successful clinical trials, the project already includes a sound commercial manufacturing strategy.European project for the development of a monoclonal antibody against Covid-19. (Read more) MAbCo19 mAb will be an invaluable remedy to protect the most vulnerable sections of the population (elderly individuals especially those with multiple comorbidities) where mortality from Covid-19 is highest; medical personnel who are at high risk of exposure, thus preserving the numerical integrity and effectiveness of health systems; immune-suppressed patients and those who may not respond to vaccination. Furthermore, mAbs will enable refined identification protective epitopes towards rational design of vaccines against Covid-19. Malaria is an acute febrile disease caused by several species of Plasmodium parasites that are transmitted by infected Anopheles mosquitos. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on the age of the individual and pre-existing immunity. Severe anaemia, respiratory distress, cerebral malaria and multiorgan failure can lead to death. In recent years there have been about 230 million annual cases of malaria worldwide, leading to over 400.000 deaths. Children aged under 5 years are the most vulnerable group affected by malaria. The WHO African Region is home to more than 90% of cases and deaths. Malaria can also be a predisposing co-morbidity for a number of other infections including fatal bacterial septicamias. Drug resistance against Plasmodium parasites is widespread and resistance to insecticides posed difficulties to control of the mosquito transmission vectors. AchilleS Vaccines aims to move away from traditional approaches and use multidisciplinary, combinatorial, innovative science towards malaria vaccine development. The MalOMVax project will exploit advanced clinical-immunology-guided reverse vaccinology, combined to the fllexible mOMV platform, to deliver antigens able to induce protective immunity against a broad range of Plasmodium parasites. New antigens and epitopes that can be recognized by immune B-cells of “protected” individuals from endemic areas will be identified, prioritized for functional protective activity, further engineered for optimal immunogenicity and displayed on the mOMV platform. Our approach will maximize the chances of developing a novel mOMV-based malaria vaccine capable of eliciting strong immunity against multiple parasite antigens and providing long-lasting protection. The project will be performed as a collaboration between AchilleS vaccines (Siena, Italy) and the National Institute of Molecular Genetics (Milan, Italy). Salmonella is a bacterium that causes life-threatening diseases in adults and children. Typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever and invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella infections (iNTS) have a high incidence worldwide (around 30 million people are affected each year worldwide, with a mortality rate of between 10 and 20%). These diseases coexist in many geographical areas, particularly in Low and Middle Income Countries (LMIC). A single vaccine against all major Salmonella infections is therefore highly desirable, given that the current ones require multiple doses and / or show moderate protective ability and some of them are expensive to produce. In addition, there is no iNTS or paratyphoid fever vaccine today. Thanks to the AV skills and the services made available by the partner ARTES 4.0, the Department of Excellence of Biotechnology, Chemistry and Pharmacy of the University of Siena, the SHASI project intends to a mathematical-digital 4.0 method aimed at identifying on the basis probabilistic the best path on which to direct pre-clinical research, the development of the vaccine prototype, the design of the clinical test and the subsequent production of the vaccine (with a reduction of times and costs and improvement of the safety of the drug), in this case of the multivalent vaccine against diseases generated by the Salmonella bacterium. The project focuses on the integration of new tools: artificial intelligence for vaccine research and the mOMV platform (modified Outer Membrane Vesicles) for its production. The output of this project will later be used to optimize the research and industrialization of the vaccine, so that the main asset is finally the patenting of the vaccine candidate at phase 1 of clinical test, so as to be resale to a pharmaceutical company able to bear the costs of the subsequent trial phases and bring it to the market. In reaching the scientific and economic objective, the growth of competence of the development team and the strengthening of the company and of the so-called Siena Vaccines Hub are implicitly achieved, i.e. the academic-productive ecosystem that makes this geographical area one of the most relevant world centers in the vaccine sector.
Obiettivo Il progetto Laboratorio 4.0 si propone di realizzare un nuovo modello di quello che è il primo stadio di sviluppo di nuovi prodotti biofarmaceutici (in particolare quelli composti da proteine ricombinanti – es. vaccini, immunosoppressori, frammenti anticorpali Fab, etc.), ovvero un nuovo modello di “ricerca e sviluppo preclinico” basato sul concetto di sviluppo “by design”, unendo competenze industriali e accademiche in campo biotecnologico e informatico. Risultati attesi L’obiettivo finale del progetto è l’abbattimento dei costi di sviluppo preclinico e miglioramento qualitativo e di efficacia di farmaci biotecnologici e vaccini, tramite una razionale ottimizzazione e la riduzione dei tempi e dei processi di sviluppo attualmente necessari. Si ipotizza che l’uso di un laboratorio fortemente informatizzato possa ridurre fino al 20% i tempi tecnici di laboratorio. Risultati ottenuti Alla conclusione del progetto, si stima una riduzione delle attività almeno pari al 20% grazie alla velocità di ricerca ottenuta, per un impatto pari a circa il 6% dovuto alla piattaforma AI, che porta l’impatto complessivo al 18% del totale, raggiungendo sostanzialmente i risultati che ci si attendeva.

Special Project – EU Malaria Fund
Categories :
Despite decades of intense research in the field, a protective, effective, and affordable vaccine has yet to be developed.
Categories :


Categories :

ASSE 1 – Priorità di investimento 1b – Azione 1.1.3
Fondo Crescita sostenibile- Accordo Innovazione Scienze della vita DM 5/03/2018
Progetto N° F/180020/01-04/X43
Cup: B69J23000110005
Avvio: 09/2020
Durata: 36 mesi
Partner: Imola Informatica S.P.A, Università degli Studi di Siena, Sis-ter S.r.l SB
Categories :